Electromagnetic Attraction Relay:
In Electromagnetic Attraction Relays, there is a coil which energises an electromagnet.When the operating current becomes large, the magnetic field produced by an electromagnet is so high that it attracts the armature or plunger, making contact with the trip circuit contacts.These are the simplest type of relays.
The various types of electromagnetic attraction type relays are
1. Attracted armature relay
2. Solenoid and plunger type relay
Attracted Armature Type Relay:
There are two types of structures available for attracted armature type relay which are,
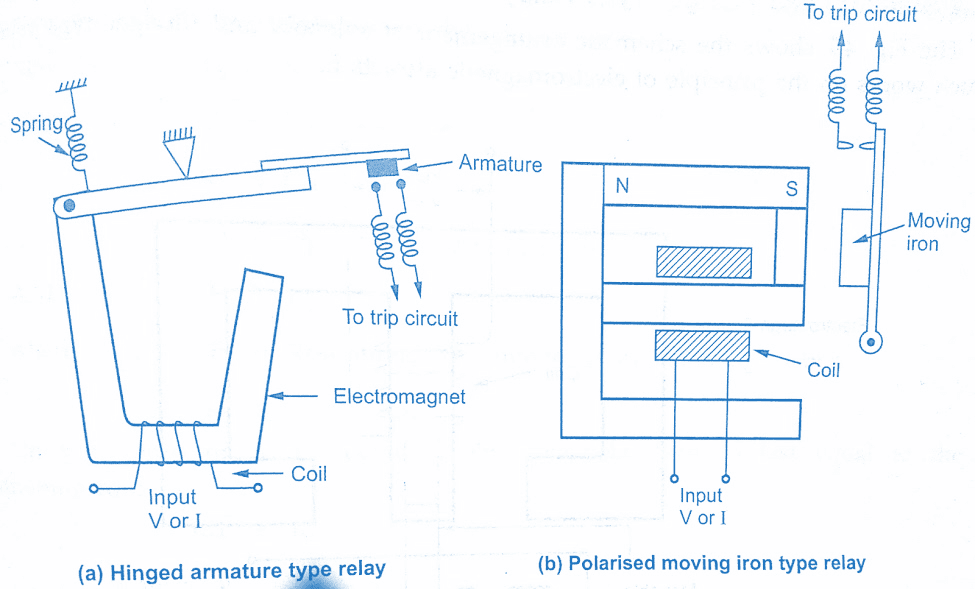
i) Hinged armature type
ii) Polarised moving iron type
The two types of attracted armature type relays are shown in the Figure(a) and (b).In attracted armature type, there exists a laminated electromagnet which carries a coil. The coil is energised by the operating quantity which is proportional to the circuit voltage or current. The armature or a moving iron is subjected to the magnetic force produced by the operating quantity. The force produced is proportional to the square of current hence Electromagnetic Attraction Relays relays can be used for a.c as well as d.c.
The spring is used to produce restraining force. When the current through coil increases beyond the limit under fault conditions, armature gets attracted. Due to this, it makes contact with contacts of a trip circuit, which results in an opening of a circuit breaker. The minimum current at which the armature gets attracted to close the trip circuit is called pickup current.
Generally, the number of tappings are provided on the relay coil with which its turns can be selected as per the requirement.This is used to adjust the set value of an operating quantity at which relay should operate.
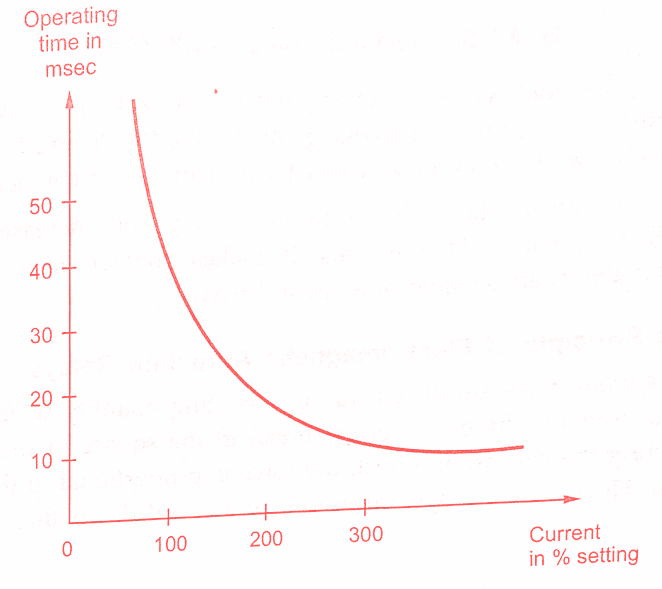
An important advantage of such relays is their high operating speed. In modern relays an operating time as small as 0.5ms is possible. The current-time characteristics of such relays is hyperbolic, as shown in the figure below.
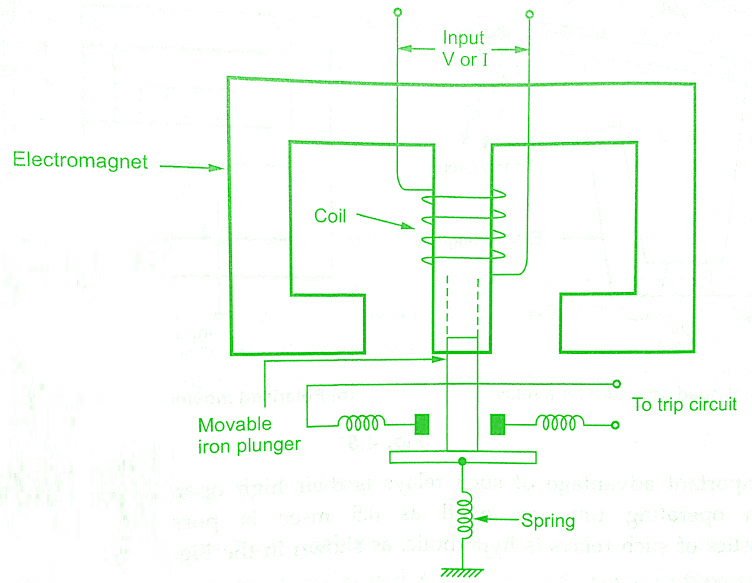
Solenoid and Plunger Type Relay:
The below figure is Solenoid and Plunger Type Relay which works on the principle of electromagnetic attraction.
It consists of a solenoid which is nothing but an electromagnet. It also consists a movable iron plunger. Under normal working conditions, the spring holds the plunger in the position such that it cannot make contact with trip circuit contacts.
Under fault conditions, when the current through relay coil increases, the solenoid draws the plunger upwards. Due to this,it makes contact with the trip circuit contacts, which results in an opening of a circuit breaker.
Operating Principle of Electromagnetic Attraction Relays:
The electromagnetic force produced due to the operating quantity which is exerted on the armature, moving iron or plunger is proportional to the square of the flux in the air gap. Thus neglecting the saturation effect, the force is proportional to the square of the operating current. Hence such relays are useful for a.c and d.c both.
For d.c operation :
In d.c. operation, the electromagnetic force is constant. When this force exceeds the restraining force, the relay operates.
Now Fe = K1 I²
where Fe = Electromagnetic force
K1 = Constant
I = Operating current in a coil
And Fr = K2
where Fr = Restraining force due to spring including friction
K2 = Constant
On the verge of relay operating, the electromagnetic force is just equal to the restraining force.
This is the current at which relay operates in case of d.c operation.
For a.c. operation : In a.c. electromagnetic relays, the electromagnetic for proportional to square of the current but it is not constant. It is given by,
where Im = Maximum value of the operating current
K = Constant
It shows that the electromagnetic force consists of two components,
i) Constant, independent of time.
ii) Pulsating at double the frequency of applied voltage.
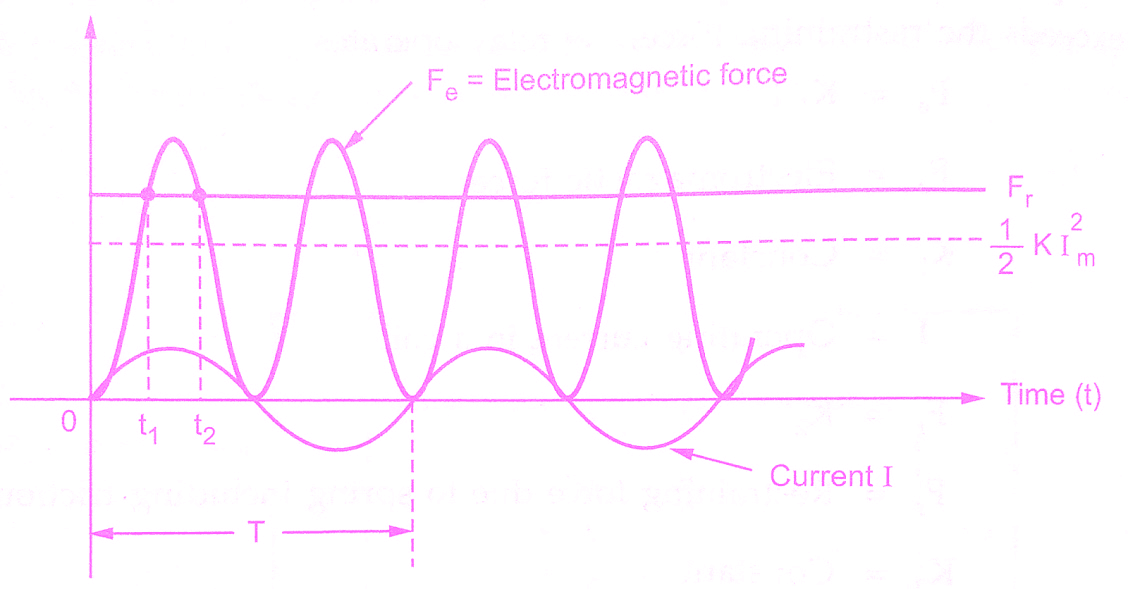
The total force thus pulsates at double the frequency. If the restraining force Fr which is produced by the spring is constant then the armature of relay will be picked up at time t1 and it drops off at time t2 as shown in the below figure.
Thus relay armature pulsates at double frequency. This causes the relay to hum and produces a noise. It may cause damage to the relay contacts. To overcome this difficulty, the air gap flux producing an electromagnetic force is divided into two fluxes acting simultaneously but differing in time phase.
This causes resulting electromagnetic force to be always positive. If this is always greater than restraining force Fr then armature will not vibrate. The phase lag between the two components of flux can be easily produced using shading in a relay. The flux through the shaded pole lags behind the flux through the unshaded part.
Advantages of Electromagnetic Relays:
The various advantages of electromagnetic relays are
1. Can be used for both a.c. and d.c.
2. They have fast operation and fast reset.
3.Electromagnetic Attraction Relays are almost instantaneous. Though instantaneous, the operating to varies with current. With extra arrangements like dashpot, copper ring etc, slow operating and resetting times can be obtained.
4. High operating speed with operating time in few milliseconds also can be achieved.
5. The pickup can be as high as 90-95% for d.c. operation and 60 to 90% for the d.c. operation.
6. Modern relays are compact, simple, reliable and robust.
Disadvantages of Electromagnetic Relays:
The few disadvantages of Electromagnetic Attraction Relays are,
1. The directional feature is absent.
2. Due to fast operation the working can be affected by the transients. As transients contain d.c. as well as pulsating component, under steady state value less than set value, the relay can operate during transients.
Applications of Electromagnetic Relays:
The various applications of Electromagnetic Attraction Relays are,
1.The protection of various a.c. and d.c. equipments.
2.The over/under current and over/under voltage protection of various a.c. and d.c. equipments.
3.In the definite time lag over current and earth fault protection along with definite time lag over current relay.
4.For the differential protection.
5.Used as auxiliary relays in the contact systems of protective relaying schemes.
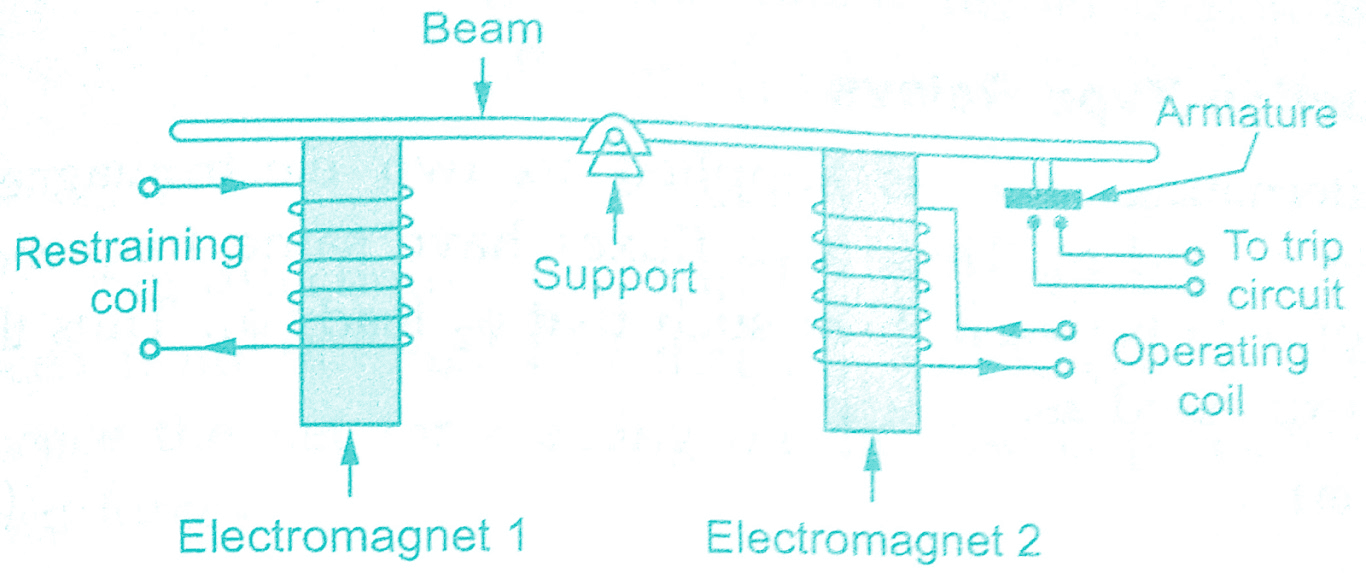
Balanced beam relay:
The balanced beam relay is also a type of attracted armature type relay. It consists of a beam carrying two electromagnets at its ends. One electromagnet produces operating torque while the other produces restraining torque. The beam is supported at the middle.
Under normal operating conditions, the two torques are equal and beam remains horizontal.The construction is shown in the above figure. When there is a fault, the operating current is high and produces high operating torque. Thus the beam gets deflected more on operating side.
Due to this, armature fitted at end of the beam gets pulled and makes contact with the contacts of trip circuit. Thus the trip circuit operates. It is robust and fast in operation. Generally only one cycle is enough for the operation. But due to the d.c transients, it is not accurate. Now a days, this type of relay is not used.
Conclusion:
Today we have learnt about Electromagnetic Attraction Relays – Working ,Construction & Types. You can download this article as pdf, ppt.

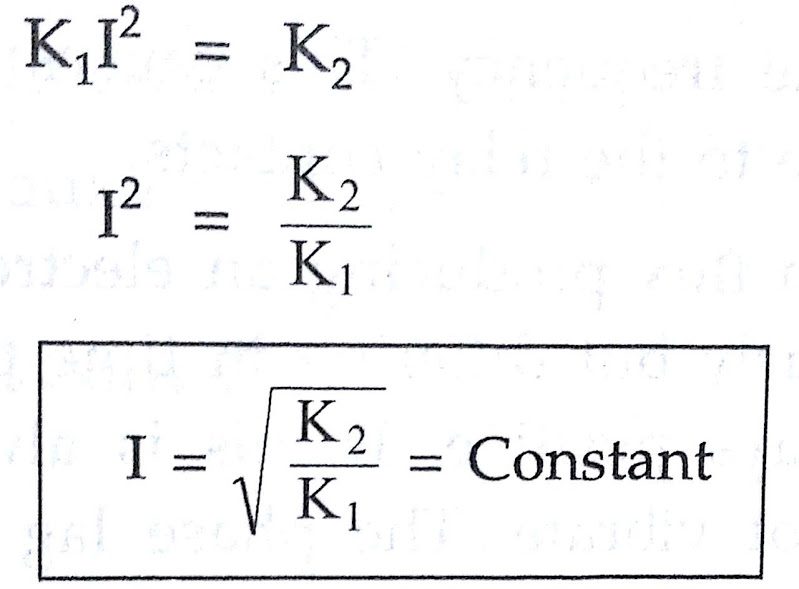
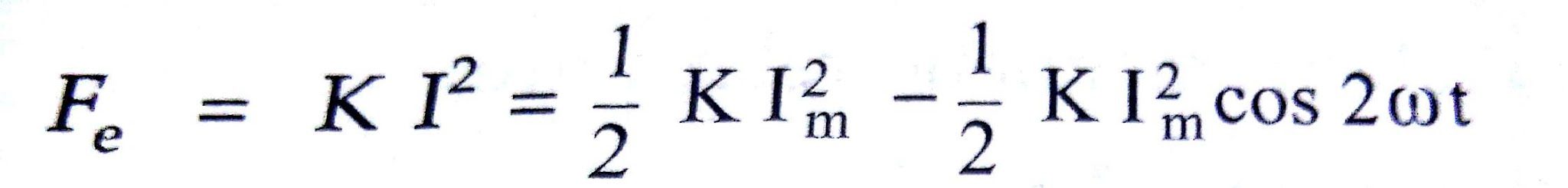
How can i download the above topic as pdf