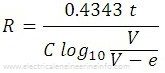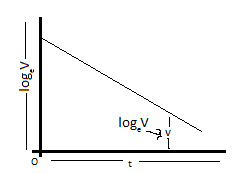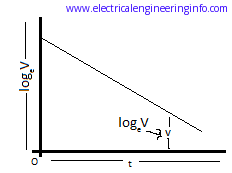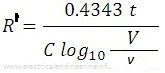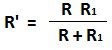Loss of Charge Method:
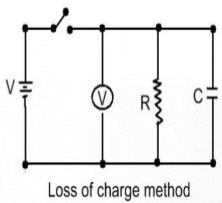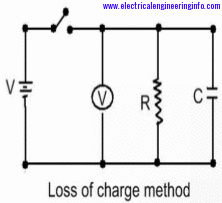
In ‘Loss of charge method‘ the insulation resistance R to be measured is connected in parallel with a capacitor C and an electrostatic voltmeter. The capacitor is charged to some suitable voltage, by means of a battery having voltage V and is then allowed to discharge through the resistance. The terminal voltage is observed over a considerable period of time during discharge.
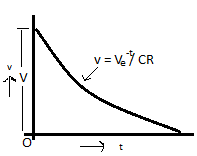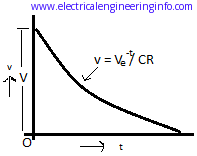
The voltage across the capacitor at any instant t after the application of voltage is
V = V exp(-t/ CR)
or V/ v = exp(-t/ CR)
or Insulation resistance
R = t / {C log V/v}
= 0.4343t /{C log V/v}
Must Read:
- Measurement of Medium Resistance by Wheatstone Bridge Method
- Measurement of Medium Resistance by Substitution Method
- Kelvin Double Bridge Method for Low Resistance Measurement
The variation of voltage v with time shown in below figure:
From the equation above, it follows that if V,v, C and t are known the value of R can be computed.
This textbook “Electrical and Electronics Measurements by S. Chand” is the best in industry. Grab it now for very less price.
If the resistance R is very large the time for an appreciable fall in voltage is very large and thus this process may become time-consuming. Also the voltage-time curve will thus be very flat and unless great care is taken in measuring voltages at the beginning and end of the time ‘r’, a serious error may be made in the ratio V / v causing a considerable corresponding error in the measured value of R. More accurate results may be obtained by change in the voltage V-v directly and calling this change as e, the expression for R becomes
This change in voltage may be measured by a galvanometer.
However, from the experimental point of view, it may be advisable to determine the time t from the discharge curve of the capacitor by plotting a curve of log v against time t. This curve is linear as shown in the figure below and thus the determination of time t from this curve for the voltage to fall from V to v yields more accurate results.
This measurement of resistance by loss of charge method is applicable to some high resistances, but it requires a capacitor of a very high leakage resistance as high as the resistance being measured. The method is very attractive if the resistance being measured is the leakage resistance of a capacitor as in this case auxiliary R and C units are not required.
Actually, in this loss of charge method, we do not measure the true value of resistance since we assume here that the value of resistance of electrostatic voltmeter and the leakage resistance of the capacitor has infinite value. But in practice corrections must be applied to take into consideration the above two resistances. The figure below shows the actual circuit of loss of charge method measuring high resistance where R1 represents the leakage resistance of the capacitor. Then if R’ is the resistance of R1 and R in parallel the discharge equation for capacitance gives
The test is then repeated with the unknown resistance R, disconnected and the capacitor discharging through R1. The value of R1 obtained from this second test and substituted into the expression
in order to get the value of R.
The leakage resistance of the voltmeter, unless very high should also be taken into consideration.
Conclusion:
We have learnt Loss of Charge Method for Measurement of High Resistance.
Comment below for any Queries.